Acne: Types, Causes, Treatment & Prevention
Introduction
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions, affecting 80% of people between ages 11 and 30. It can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity, but teenagers and young adults are the most affected.
Acne doesn’t just affect your skin – it can also lead to:
- Redness and inflammation
- Rough, uneven skin texture
- Dark spots and patches
- Scarring
- Physical discomfort
Acne can also have a psychological impact, causing emotional challenges that may last long after the physical symptoms go away. Many people with acne experience:
- Low self-confidence
- Social anxiety and withdrawal
- Depression and mood swings
- Struggles in personal relationships
- Decreased performance at school or work
Dealing with acne isn’t just about treating the visible signs – it’s important to understand what’s causing it and find effective solutions. Whether you have occasional breakouts or ongoing acne issues, knowing the right treatment options can greatly help in managing this condition and boosting your confidence.
Understanding Acne: Types and Causes
Acne develops when your skin’s oil glands produce excess sebum, combining with dead skin cells to clog hair follicles. This creates an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to inflammation and various types of acne lesions.
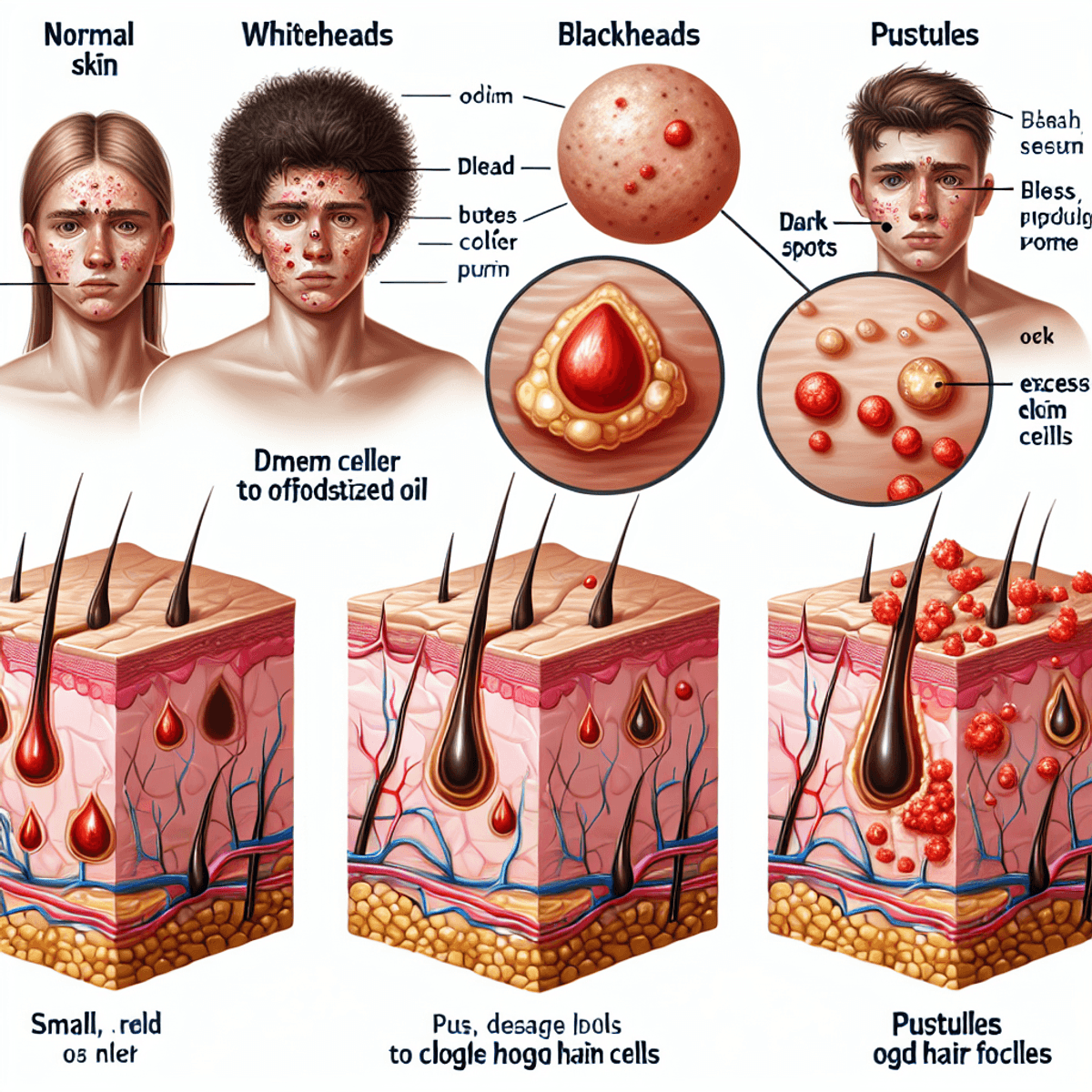
Common Types of Acne Lesions
Non-Inflammatory Lesions:
- Whiteheads (Closed Comedones): Small, flesh-colored bumps with trapped oil and dead skin cells beneath the skin’s surface
- Blackheads (Open Comedones): Dark spots caused by oxidized oil in open pores, giving them their characteristic black appearance
Inflammatory Lesions:
- Papules: Small, red, tender bumps without visible pus
- Pustules: Red bumps with white or yellowish pus at their center
- Nodules: Large, painful bumps deep under the skin
- Cysts: Deep, pus-filled lesions that can cause scarring
Primary Causes of Acne Development
Hormonal Influences:
- Increased androgen production during puberty
- Menstrual cycle fluctuations
- Pregnancy-related hormonal changes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Biological Factors:
- Excess oil production: Your sebaceous glands create too much sebum
- Dead skin cells: Irregular shedding leads to clogged pores
- Bacteria growth: P. acnes bacteria multiply within blocked follicles
- Inflammation: Your immune system responds to bacterial growth
External Triggers:
- Certain medications containing corticosteroids
- Heavy or occlusive skincare products
- Environmental factors like humidity and pollution
- Friction from tight clothing or sports equipment
The severity of acne varies significantly among individuals. While some experience mild breakouts with occasional whiteheads and blackheads, others develop severe cystic acne requiring medical intervention. Understanding your specific type of acne helps determine the most effective treatment approach.
Your genetic predisposition plays a crucial role in how your skin responds to these various triggers. If your parents experienced severe acne
Other Factors That Contribute to Acne Breakouts
Your genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining your skin’s behavior and acne susceptibility. Research shows that if both your parents experienced severe acne, you’re more likely to develop similar skin concerns. Genetics influence:
- Oil production levels in your skin
- Pore size and structure
- Inflammatory response to bacteria
- Rate of skin cell turnover
- Hormone sensitivity
Medication-Related Breakouts
Certain medications can trigger or worsen acne breakouts:
- Corticosteroids (both oral and topical)
- Testosterone supplements
- Birth control pills containing androgenic progestins
- Lithium-based medications
- Anti-epileptic drugs
- B complex vitamins in high doses
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Your Skin
Your daily habits and choices significantly impact your skin’s health:
Diet
- High glycemic foods spike insulin levels, increasing oil production
- Dairy products contain growth hormones that can trigger breakouts
- Processed foods with artificial additives may cause inflammation
- Chocolate and greasy foods don’t directly cause acne, but can worsen existing conditions
Stress Impact
- Elevated cortisol levels increase sebum production
- Stress hormones trigger inflammatory responses
- Physical stress from lack of sleep affects skin repair
- Chronic stress weakens your immune system
Sleep Patterns
- Poor sleep disrupts hormone balance
- Insufficient rest reduces skin cell regeneration
- Night-time skin repair processes require 7-9 hours of sleep
- Irregular sleep schedules affect cortisol levels
Environmental Factors
High humidity levels can trap sweat and bacteria
Air pollution deposits irritants on your skin
UV exposure can worsen acne marks and inflammation
Hard water may leave mineral deposits that clog pores
Physical Contact
Touching your face transfers bacteria
Tight clothing traps sweat and causes friction
Phone screens harbor bacteria that contact your face
Unwashed pillowcases accumulate oil and dead skin cells
Understanding these contributing factors helps you identify and modify specific triggers affecting your skin’s condition. By recognizing these elements, you can make informed decisions about lifestyle changes. For a more comprehensive understanding of the various skin diseases that may arise from such factors, it’s essential to consult a professional. Additionally, gaining insight into the symptoms and causes of acne can provide valuable information for managing this common yet challenging condition.
Effective Treatment Options for Acne Management
Managing acne requires a strategic approach tailored to your skin type and the severity of your breakouts. Let’s explore proven treatment options, starting with accessible over-the-counter solutions.
Over-the-Counter Treatments: Benzoyl Peroxide and Salicylic Acid
Benzoyl Peroxide
- Works by killing acne-causing bacteria
- Available in concentrations from 2.5% to 10%
- Best for inflammatory acne (red, swollen bumps)
- Start with lower concentrations to minimize irritation
- Apply a thin layer to affected areas
- Results typically visible within 4-6 weeks
Usage Tips:
- Use white towels and pillowcases (benzoyl peroxide can bleach fabrics)
- Apply sunscreen during the day (increases sun sensitivity)
- Begin with once-daily application
Salicylic Acid
Penetrates deep into pores to dissolve excess oil and dead skin cells, available in strengths from 0.5% to 2%, making it ideal for blackheads and whiteheads. It helps prevent future breakouts and can be used alongside benzoyl peroxide.
Best Practices:
- Start with products containing 1% concentration
- Apply to clean, dry skin
- Use consistently for optimal results
- Can be found in cleansers, toners, and spot treatments
Combination Approach
You can maximize results by combining these treatments:
- Morning: Salicylic acid cleanser followed by benzoyl peroxide spot treatment
- Evening: Gentle cleanser with salicylic acid treatment
- Allow products to fully absorb before applying moisturizer
Product Selection Tips
- Choose non-comedogenic formulations
- Look for additional soothing ingredients like aloe or niacinamide
- Consider gel formulations for oily skin
- Select cream-based products for dry or sensitive skin
Treatment Timeline
- Week 1-2: Skin adjustment period
- Week 3-4: Reduction in new breakouts
- Week 6-8: Visible improvement in existing acne
For more severe cases such as cystic acne, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist who may recommend prescription treatments or other alternatives. These could include topical retinoids, oral antibiotics, or hormonal therapies which are all part of a comprehensive acne treatment plan.
2. Prescription Medications for Moderate to Severe Cases: Oral Antibiotics and Retinoids
When over-the-counter treatments don’t provide sufficient relief, prescription medications offer stronger solutions for moderate to severe acne cases. These medications target persistent breakouts through different mechanisms:
Oral Antibiotics
- Tetracyclines (Doxycycline, Minocycline)
- Macrolides (Erythromycin)
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
These antibiotics work by:
- Killing acne-causing bacteria
- Reducing inflammation
- Preventing new breakout formation
Prescription Retinoids
- Tretinoin (Retin-A)
- Adapalene (Differin)
- Tazarotene (Tazorac)
- Isotretinoin (Accutane) – for severe cases
Retinoids deliver results by:
- Unclogging pores
- Speeding up cell turnover
- Reducing oil production
- Preventing scarring
Treatment Duration and Usage
- Antibiotics: 3-6 months typical course
- Topical retinoids: Long-term maintenance
- Isotretinoin: 4-6 months single course
Important Considerations
- Start with lower strengths to minimize irritation
- Apply sunscreen daily with retinoid use
- Regular monitoring by healthcare provider required
- Pregnancy testing for female patients on isotretinoin
- Potential side effects need discussion with doctor
Your dermatologist might combine these treatments with other options like:
- Hormonal medications for women
- Topical antibiotics
- Prescription-strength benzoyl peroxide
- Chemical peels
The success of prescription treatments depends on consistent use and following medical guidance. Many patients see significant improvement within 2-3 months of starting prescription therapy.
3. Advanced Treatments for Severe or Persistent Acne: Laser Therapy and Chemical Peels
For persistent acne cases that don’t respond to traditional treatments, advanced medical interventions can be beneficial. These specialized treatments target deeper layers of acne and help minimize scarring.
Laser Therapy Options:
- Blue Light Therapy: Kills acne-causing bacteria beneath the skin’s surface
- Photodynamic Therapy: Combines light treatment with photosensitizing medications
- CO2 Laser Resurfacing: Removes damaged skin layers and stimulates collagen production
- Pulsed Dye Laser: Reduces inflammation and redness associated with active acne
Chemical Peels for Acne Treatment:
- Superficial Peels: Contains alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs)
- Gentle exfoliation
- Unclogs pores
- Reduces minor scarring
- Medium-Depth Peels: Uses trichloroacetic acid (TCA)
- Penetrates deeper skin layers
- Treats moderate scarring
- Improves skin texture
- Deep Peels: Contains phenol
- Addresses severe scarring
- Requires longer recovery time
- Produces dramatic results
Treatment Considerations:
- Multiple sessions needed for optimal results
- Cost ranges from $150-$3000 per session
- Recovery time varies by treatment type
- Professional medical supervision required
- Results vary based on skin type and acne severity
Post-Treatment Care:
- Sun protection essential
- Gentle skincare routine
- Regular moisturizing
- Avoid picking or scratching treated areas
- Follow-up appointments for progress monitoring
These advanced treatments work best as part of a comprehensive acne management plan, combining different approaches for maximum effectiveness. Your dermatologist can create a customized treatment schedule based on your skin’s needs and response to therapy.
Natural Remedies for Acne Relief at Home
You can effectively manage acne using natural ingredients found right in your kitchen. These home remedies offer gentle yet powerful solutions for various types of acne concerns.
Tea Tree Oil
This powerful natural antiseptic contains antibacterial properties that target acne-causing bacteria. Mix 1-2 drops with a carrier oil like jojoba or coconut oil before applying directly to blemishes.
Honey
Raw honey works as a natural antibacterial agent and helps retain skin moisture. Apply a thin layer of raw, unpasteurized honey to clean skin for 15-20 minutes before rinsing with lukewarm water.
Aloe Vera
Fresh aloe vera gel reduces inflammation and promotes healing. Extract the gel directly from an aloe plant or use pure aloe vera gel, applying it as a spot treatment or all-over face mask.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Create a natural toner by diluting apple cider vinegar with water (1:3 ratio). This solution helps balance skin pH and contains natural acids that exfoliate dead skin cells.
DIY Face Masks
Turmeric + Yogurt Mask
- 1 teaspoon turmeric powder
- 2 tablespoons plain yogurt
- Apply for 15 minutes
- Benefits: Anti-inflammatory properties, reduces redness
Green Tea + Honey Mask
- 1 green tea bag (brewed and cooled)
- 1 tablespoon honey
- Mix into a paste
- Benefits: Antioxidant protection, reduces sebum production
Natural Spot Treatments
Cinnamon + Honey Paste
- Equal parts cinnamon and honey
- Apply directly to blemishes
- Leave overnight
- Benefits: Antibacterial properties, reduces inflammation
Lemon Juice
- Dilute fresh lemon juice with water
- Apply with a cotton swab
- Use only at night
- Benefits: Natural astringent, lightens acne marks
Essential Tips for Natural Treatment
- Patch test new ingredients on your inner arm before facial application
- Use organic, pure ingredients whenever possible
Preventive Measures To Keep Your Skin Clear From Future Breakouts
Daily Skincare Routine: Non-Comedogenic Products And Gentle Cleansing Techniques
A consistent skincare routine forms the foundation of acne prevention. You’ll need specific products and techniques to maintain clear, healthy skin.
Essential Non-Comedogenic Products:
- Gentle Cleanser: Use a pH-balanced, sulfate-free cleanser twice daily
- Oil-Free Moisturizer: Apply lightweight, water-based formulas
- Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Choose SPF 30+ products labeled “non-comedogenic”
- Treatment Products: Include spot treatments containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide
Effective Cleansing Techniques:
- Start with clean hands to avoid transferring bacteria
- Use lukewarm water – hot water strips natural oils
- Apply cleanser in gentle circular motions
- Limit washing to twice daily to prevent irritation
- Pat dry with a clean towel – never rub
Product Application Order:
- Cleanser
- Toner (if using)
- Treatment products
- Moisturizer
- Sunscreen (morning routine)
Key Prevention Practices:
- Change pillowcases weekly
- Clean phone screens regularly
- Keep hair products away from face
- Remove makeup before bed
- Use fresh towels for face-drying
Signs You’re Over-Cleansing:
- Tight, squeaky-clean feeling
- Increased oil production
- Redness or irritation
- Flaking or peeling
- Sudden breakouts
Your skin needs time to adjust to new products. Introduce one product at a time, waiting 1-2 weeks before adding another. This method helps identify which products work best for your skin type.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Using harsh scrubs
- Touching face frequently
- Applying thick, heavy products
- Skipping moisturizer
- Using dirty makeup brushes
A gentle approach yields better results than aggressive treatments. Your skin’s natural barrier needs protection while fighting acne. Stick to your routine consistently –
Conclusion
Your battle against acne extends beyond skincare products – lifestyle choices play a crucial role in maintaining clear, healthy skin. Let’s explore the essential strategies you need to prevent breakouts and achieve lasting results.
Stress Management Techniques for Clear Skin:
- Practice daily meditation or deep breathing exercises
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Set realistic goals and boundaries
- Try journaling to process emotions
- Schedule regular breaks during work
- Consider professional counseling when needed
Sleep Hygiene Practices That Support Skin Health:
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
- Create a dark, cool sleeping environment
- Use clean pillowcases (change them 2-3 times weekly)
- Avoid screens 1-2 hours before bedtime
- Remove makeup before sleeping
- Stay hydrated throughout the day
Additional Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Track your acne triggers in a diary
- Balance your hormones through regular exercise
- Practice mindful eating habits
- Stay consistent with your chosen treatments
- Be patient – results take time
Remember, your skin reflects your internal health. High stress levels trigger cortisol production, leading to increased oil production and inflammation. Quality sleep allows your skin to repair and regenerate, while poor sleep habits can disrupt hormone balance and compromise your skin’s protective barrier.
These lifestyle changes work best when combined with proper skincare routines and appropriate treatments. You’ll notice improvements in both your skin’s appearance and your overall well-being when you prioritize stress management and healthy sleep patterns.
Start implementing these changes gradually – pick one or two habits to focus on initially. Your skin’s health is a journey, not a race. Stay committed to these practices, and you’ll create a strong foundation for clear, resilient skin.
Conclusion: Taking a Holistic Approach to Achieve Clearer Skin
Treating acne requires a well-rounded strategy that addresses both internal and external factors. Understanding the different types of acne – from whiteheads to cystic lesions – helps you identify the most effective treatment approach for your specific condition.
Your journey to clearer skin starts with:
- Consistent Skincare Routine: Implementing a daily regimen using non-comedogenic products
- Targeted Treatments: Choosing appropriate solutions based on your acne type
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adjusting diet, sleep patterns, and stress management techniques
- Professional Guidance: Seeking dermatological expertise for persistent cases
The path to acne-free skin extends beyond spot treatments. A holistic approach combines medical interventions with lifestyle adjustments, creating lasting results. This strategy proves particularly effective for addressing various skin concerns:
- Removing stubborn bumps on arms and legs
- Eliminating facial blemishes
- Reducing post-inflammatory red marks
- Minimizing acne scars
Your skin’s health reflects your body’s internal balance. By integrating proper skincare practices with healthy lifestyle choices, you create an environment where clear skin can thrive. This comprehensive approach not only treats existing breakouts but builds a foundation for long-term skin health.
Remember that successful acne management requires patience and consistency. The combination of targeted treatments, preventive measures, and lifestyle modifications creates a powerful strategy for achieving and maintaining clear, healthy skin.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is acne and how does it manifest on the skin?
Acne is a common skin condition that primarily affects teenagers and young adults. It manifests on the skin in various forms, including whiteheads, blackheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
What psychological impacts can acne have on individuals?
Acne can significantly impact an individual’s psychological well-being, leading to issues such as low self-esteem and social anxiety due to the visible nature of the condition.
What are some common factors that contribute to acne breakouts?
Factors contributing to acne breakouts include hormonal changes (especially during puberty), genetics, certain medications (like corticosteroids), and lifestyle influences such as diet, stress levels, and sleep patterns.
What over-the-counter treatments are effective for mild acne?
Common over-the-counter treatments for mild acne include benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid. These ingredients help reduce inflammation and unclog pores.
What prescription medications are available for moderate to severe acne?
For moderate to severe cases of acne, prescription medications such as oral antibiotics and retinoids are often recommended. These treatments help control bacteria and promote skin cell turnover.
Are there advanced treatment options for severe or persistent acne?
Yes, advanced treatment options for severe or persistent acne include laser therapy and chemical peels. These methods aim to reduce inflammation and improve skin texture by targeting deeper layers of the skin.










