How to prevent acne: What triggers it and what helps

Introduction
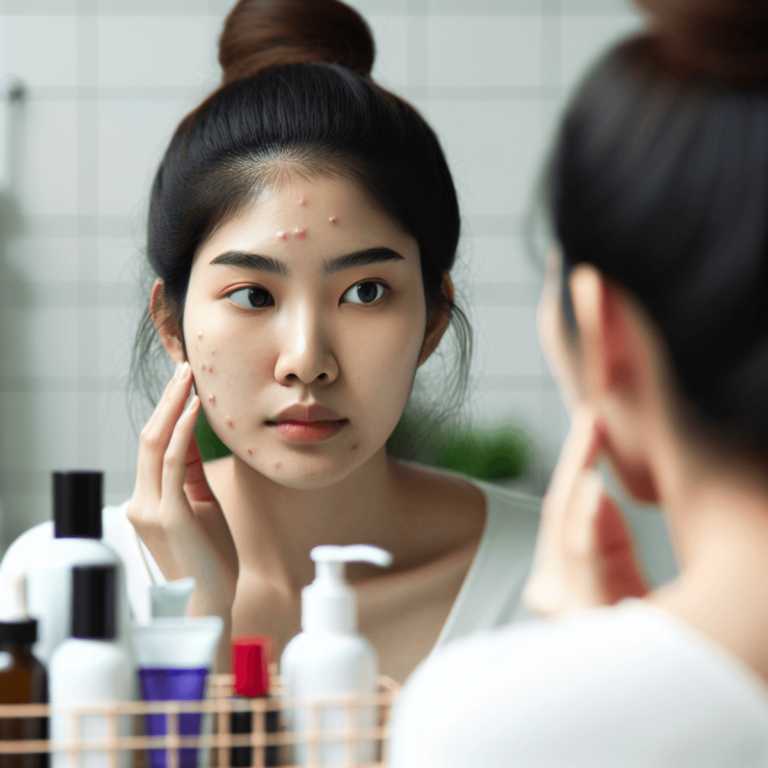
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions affecting millions worldwide. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, resulting in various types of pimples such as blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts. While it primarily impacts teenagers and young adults, many adults continue to experience breakouts.
Understanding the triggers that contribute to acne is crucial for effective prevention. By identifying specific factors such as hormonal fluctuations, dietary influences, environmental conditions, and lifestyle choices, you can take proactive steps to minimize breakouts.
This article will explore:
- What acne is: A closer look at its characteristics and types.
- Common triggers: Insight into factors that may cause or worsen acne.
- Preventive measures: Practical tips on how to prevent pimples through skincare routines and healthy habits.
By gaining knowledge about these aspects, you empower yourself to adopt strategies that can help reduce pimples and achieve clearer skin. Understanding how to prevent acne is not just about treating existing issues; it’s about fostering long-term skin health.
Understanding Acne
Acne is a common skin condition that appears in different forms of pimples. It mainly occurs when hair follicles get blocked with oil (sebum), dead skin cells, and bacteria. Knowing the features of acne helps us understand how to manage and prevent it.
Characteristics of Acne
- Clogged Hair Follicles: The main reason why acne develops. When hair follicles are blocked, it creates a favorable environment for bacteria to grow.
- Inflammation: Usually, clogged follicles cause inflammation, leading to redness and swelling around the affected area.
- Variety of Lesions: Acne can show up in many ways, from mild to severe cases.
Types of Acne
- Blackheads: Open comedones that appear black on the surface due to oxidation. These occur when a hair follicle is only partially clogged.
- Whiteheads: Closed comedones formed when a follicle is completely blocked. They appear as small white bumps under the skin’s surface.
- Cysts: Deep, inflamed lesions filled with pus. Cysts can be painful and often require professional treatment due to their severity.
How Hair Follicles Become Clogged
Clogging happens through several processes:
- Excess Oil Production: Hormonal changes often lead to increased sebum production, which can overwhelm the follicle’s capacity.
- Dead Skin Cells: Inadequate exfoliation allows dead skin cells to build up, contributing to blockages.
- Bacteria Growth: Propionibacterium acnes is a bacteria that thrives in clogged follicles, worsening inflammation and leading to more severe breakouts.
Understanding these types and processes behind acne explains why effective treatment methods focus on reducing oil production, improving skin cell turnover, and controlling bacterial growth.
Common Triggers of Acne and How to Avoid Them
Hormonal Fluctuations: Understanding the Role of Hormones in Acne Development
Acne is significantly influenced by hormonal fluctuations, which play a crucial role in its development. Hormones, particularly androgens such as testosterone, are known to stimulate oil (sebum) production in the skin. Increased oil production can lead to clogged hair follicles, creating an environment that fosters acne growth.
Role of Hormones in Acne Development
- Androgens: These male hormones are present in both men and women. Elevated androgen levels can lead to:
- Increased sebum production
- Enlarged sebaceous glands
- Higher likelihood of clogged pores
- Estrogen: In women, fluctuations in estrogen during menstrual cycles can impact acne. A drop in estrogen levels may cause an increase in androgens, exacerbating oil production and leading to breakouts.
- Progesterone: This hormone rises during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle. Its presence can also trigger increased oiliness and inflammation, further contributing to acne flare-ups.
Understanding these hormonal influences is essential for recognizing why some individuals experience more severe acne at certain times, such as during puberty or menstrual cycles. For instance, conditions like PCOS can also lead to severe hormonal imbalances resulting in persistent acne.
Impact of Puberty and Hormonal Changes in Women
Puberty is a significant period when hormonal changes occur. Both boys and girls experience an increase in androgen levels, resulting in:
- Increased Oil Production: The surge of hormones during puberty often means that sebaceous glands become more active, leading to oily skin.
- Higher Breakout Incidence: Many teenagers find themselves with numerous blackheads, whiteheads, and inflamed cysts due to this heightened oil production.
For women, hormonal changes continue throughout life stages such as:
- Menstrual Cycle: Many women notice a cyclical pattern of breakouts that corresponds with their menstrual cycle. Pre-menstrual acne is common due to fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal shifts can either alleviate or worsen acne for some women during pregnancy depending on individual body responses.
Dietary Factors: The Link Between Food and Acne Breakouts
Diet plays a pivotal role in maintaining healthy skin. Certain foods may exacerbate acne by increasing insulin levels or promoting inflammation. Key dietary factors include:
- Dairy Products: Milk and dairy may affect hormone levels linked to acne development. Studies suggest that dairy consumption correlates with higher rates of acne among adolescents.
- High-Sugar Foods: Foods high in sugar can lead to spikes in insulin. This spike may trigger increased oil production and inflammation.
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support your skin health while potentially reducing the risk of breakouts. However, it’s important to note that not all dietary advice is accurate; there are many myths surrounding diet and acne that should be clarified.
Environmental Influences: How Your Surroundings Can Affect Your Skin Health
Environmental factors contribute significantly to skin conditions like acne. Pollutants and climate conditions interact with the skin’s surface leading to increased chances of clogged pores:
- Air Pollution
Dietary Factors: The Link Between Food and Acne Breakouts
Understanding the connection between dietary factors and acne is essential for managing this common skin condition. Certain foods can worsen acne breakouts, making it crucial to be mindful of your diet.
Foods to Avoid
- Dairy Products: Milk and cheese have been linked to increased acne in some individuals. Dairy may influence hormone levels, leading to heightened oil production and clogged pores.
- High-Sugar Foods: Foods loaded with sugar can cause spikes in insulin levels, which may promote the secretion of hormones that trigger oil production. This can create an environment conducive to acne development.
The relationship between diet and skin health is complex yet significant. Research has indicated that a high-glycemic index diet may lead to more severe acne compared to a balanced diet rich in whole foods. Foods that are processed or high in refined carbohydrates may contribute to inflammation, further aggravating the condition.
Practical Tips for Minimizing Exposure to Dietary Triggers
- Opt for Whole Foods: Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These foods provide essential nutrients that support skin health.
- Monitor Dairy Intake: Consider reducing or eliminating dairy products from your diet to see if there is an improvement in your skin condition.
- Limit Sugar Consumption: Try to cut back on sugary snacks and beverages. Instead, choose healthier alternatives like fruits or nuts.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain skin elasticity and aids overall skin health.
By understanding how dietary factors contribute to acne breakouts, you can take proactive steps toward clearer skin. Adjusting your eating habits can be an effective part of your strategy in combating this frustrating condition while promoting overall well-being.
Environmental Influences: How Your Surroundings Can Affect Your Skin Health
Environmental factors play a significant role in acne formation. Understanding how these influences can trigger breakouts is essential for effective prevention strategies.
Key Environmental Triggers:
- Air Pollution: The presence of pollutants such as soot, dust, and chemicals in the air can contribute to skin irritation and clogged pores. Pollutants may interact with oil and dead skin cells, exacerbating acne.
- Humidity: High humidity levels can increase sweat and oil production. This excess moisture creates an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to more breakouts. Conversely, low humidity can lead to dry skin, prompting an increase in oil production as the skin tries to compensate.
- Greasy Products: Exposure to oily or greasy substances from cosmetics, hair products, or even cooking oil can clog pores. When these products come into contact with your skin, they may lead to inflammation and acne.
- Face Masks: While face masks are essential for health safety, they can also cause skin problems if not used properly. The constant friction and trapped moisture can lead to increased breakouts.
Practical Tips for Minimizing Exposure:
- Cleansing Routine: Use a gentle cleanser daily to remove dirt and pollutants from your skin. Consider using a foaming cleanser that targets oil without stripping moisture.
- Protective Barriers: Apply non-comedogenic moisturizers and sunscreen to protect your skin from environmental stressors while preventing clogged pores.
- Limit Outdoor Exposure: On days with high pollution levels or extreme humidity, try to minimize outdoor activities. If you must go outside, consider wearing protective clothing or a mask.
- Regularly Wash Hair and Face: Keeping hair clean helps reduce the transfer of oils and products onto your face. Washing your face after sweating helps eliminate excess oils that may contribute to breakouts.
- Choose Products Wisely: Opt for makeup and skincare products that are labeled as non-comedogenic and avoid heavy formulations that may exacerbate acne.
By recognizing the impact of environmental influences on your skin health, you can take proactive steps to manage these triggers effectively. Awareness of these factors is crucial in your journey on how to prevent acne: what triggers it and what helps.
Lifestyle Choices: The Impact of Stress Management and Medications on Acne Breakouts
Stress and Acne
Stress plays a significant role in the development of acne. When you’re stressed, your body releases cortisol, a hormone that can trigger increased oil production in the skin. This heightened oil production can lead to clogged pores, creating an environment where bacteria thrive, resulting in breakouts.
Practical tips for managing stress:
- Practice mindfulness: Meditation and deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels.
- Engage in physical activity: Regular exercise not only boosts mood but also helps regulate hormones.
- Establish a healthy sleep routine: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support skin health.
Medications That Can Trigger Outbreaks
Certain medications may contribute to acne flare-ups. These include:
- Hormonal treatments: Some birth control pills or hormone replacement therapies can affect oil production.
- Steroids: Corticosteroids may exacerbate acne by influencing hormone levels and oil gland activity.
- Antidepressants: Certain types can lead to increased sebum production.
If you suspect that your medication is impacting your skin, consult with your healthcare provider about potential alternatives or adjustments.
Habits to minimize medication-related breakouts:
- Communicate with your doctor: Discuss any skin changes after starting new medications.
- Monitor your diet: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants can counteract some side effects of medications.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports overall skin health and helps flush out toxins.
Understanding these lifestyle factors provides valuable insights into how to prevent acne effectively. By managing stress and being aware of the effects of certain medications, you can take proactive steps to maintain clearer skin. Addressing these triggers is essential as you navigate through hormonal fluctuations, dietary factors, and environmental influences that may also affect your complexion.
Effective Preventive Measures for Acne Control at Home
Makeup Tips for Acne-Prone Skin: Choosing Non-Comedogenic Products and Application Techniques That Won’t Clog Pores
For individuals with acne-prone skin, selecting the right makeup products and application techniques is crucial. Using non-comedogenic makeup can significantly reduce the risk of clogged pores, which leads to breakouts. Consider the following guidelines:
1. Opt for Non-Comedogenic Formulations
Always choose products labeled as non-comedogenic. This means they are specially formulated not to block pores. Look for foundations, concealers, and powders that are oil-free and designed for sensitive skin.
2. Check Ingredients Carefully
Avoid products containing heavy oils or silicones, which can exacerbate acne. Instead, seek lightweight formulas that include beneficial ingredients like salicylic acid or niacinamide. These can help manage oil production while providing coverage.
3. Use Mineral Makeup
Mineral makeup often contains natural ingredients that can be gentler on the skin. It provides good coverage without clogging pores. Look for mineral-based foundations or powders that also offer sun protection.
4. Application Techniques Matter
How you apply makeup can impact your skin health. Use clean brushes or sponges to avoid transferring bacteria and oils from your hands onto your face.
- Dab rather than rub: When applying concealer or foundation, gently dab instead of rubbing it into the skin. This technique minimizes irritation and helps maintain a smoother finish.
5. Avoid Heavy Layering
Layering multiple products can lead to a cakey appearance and increase the likelihood of breakouts. Instead, try using a tinted moisturizer or BB cream for light coverage when possible.
6. Set Your Makeup Wisely
If you use powder to set your makeup, opt for translucent powders that do not contain added oils. These allow your skin to breathe while controlling shine throughout the day.
7. Regularly Clean Your Makeup Tools
Brushes and sponges should be washed regularly to prevent bacteria buildup. A simple solution of mild soap and water works well; ensure they are completely dry before using them again.
In addition to choosing the right products, maintaining an effective skincare routine plays a vital role in keeping acne at bay:
- Cleanse Gently Twice Daily: Use a gentle cleanser suitable for acne-prone skin to remove impurities without stripping essential moisture.
- Moisturize Appropriately: Even oily skin needs hydration. Choose lightweight, oil-free moisturizers that won’t contribute to breakouts.
- Exfoliate Regularly: Incorporating chemical exfoliants like alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs) can help unclog pores and promote cell turnover without physical scrubbing.
By implementing these makeup tips alongside a consistent skincare routine, individuals with acne-prone skin
Healthy Habits for Clearer Skin: Practicing Good Hygiene and Avoiding Irritants Like Alcohol-Based Products or Harsh Skincare Formulations
Maintaining a consistent skincare routine is crucial for preventing acne breakouts. Here are essential practices to incorporate into your daily regimen:
1. Gentle Cleansing
Use a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser twice daily. This helps remove excess oil and dead skin cells without irritating the skin.
2. Regular Face Washing
Wash your face after sweating, especially after exercise. Sweat can mix with oil and dirt, leading to clogged pores.
3. Avoiding Irritants
Steer clear of alcohol-based products. These can strip the skin of moisture, prompting it to produce more oil and potentially worsening acne.
4. Choosing the Right Products
Look for skincare formulations labeled as “non-comedogenic.” This ensures they won’t clog your pores. Recommended ingredients include:
- Benzoyl peroxide
- Salicylic acid
- Niacinamide
Incorporate these healthy habits into your daily routine for clearer skin. Consistency is vital; don’t skip steps even when your skin appears clear. Prioritize hydration and gentle care to create an environment where your skin can thrive without irritation.
When to Seek Professional Help for Persistent Breakouts?
Persistent acne requires careful attention and, in some cases, professional intervention. Understanding when to seek help can lead to effective treatment options that address your unique skin needs.
Topical Medications
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against acne. Commonly used products include:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This powerful ingredient works by killing bacteria and reducing oil production. It is available in various forms such as gels, creams, and lotions.
- Salicylic Acid: An effective treatment that helps unclog pores and reduce inflammation. It is typically found in cleansers, toners, and spot treatments.
Consider using these medications consistently for several weeks before evaluating their effectiveness. If no improvement is noticed, it may be time to explore other options.
Oral Medications
For moderate to severe acne, oral medications might be necessary. These include:
- Antibiotics: Such as tetracycline or doxycycline, help reduce bacteria and inflammation from within the body. They are usually prescribed for a limited period to avoid antibiotic resistance.
- Hormonal Therapy: Particularly beneficial for women experiencing hormonal fluctuations related to menstrual cycles. Birth control pills containing estrogen and progestin can regulate hormones that trigger acne.
Consulting with a dermatologist about these options can help create a tailored treatment plan based on your specific condition.
Advanced Treatment Options
For those who do not respond well to topical or oral medications, advanced treatments may offer relief:
- Laser Therapy: Targets bacteria and reduces oil production through focused light beams. This method minimizes scarring while promoting clearer skin.
- Chemical Peels: Involves applying a solution that removes the top layer of skin, revealing smoother skin underneath. Chemical peels help reduce the appearance of scars and blemishes.
These options may require multiple sessions for optimal results but can significantly improve skin clarity in persistent cases.
Natural Remedies for Pimples
While professional treatments are effective, various home remedies may also help in controlling acne:
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antibacterial properties, it can be applied directly to pimples or mixed with a carrier oil.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Offers soothing effects while helping to heal wounds and reduce inflammation.
Incorporating these natural remedies into your skincare routine may provide additional support alongside professional treatments.
Lifestyle Modifications
Integrating lifestyle changes plays a crucial role in long-term acne management:
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Stress can exacerbate acne breakouts due to increased hormone production. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can significantly lower stress levels.
- Dietary Adjustments: Evaluate your food intake. Limiting dairy products and high-sugar foods may contribute positively to skin health. Incorporate more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet for better overall skin appearance.
Regularly consulting with a healthcare provider ensures you stay informed about new treatments and remedies tailored specifically for you. Taking proactive steps toward managing your acne will enable you to achieve clearer skin effectively.
Remember that understanding how to get rid of pimples requires patience and persistence. Whether exploring topical or oral medications or considering advanced treatment options, combining these methods with healthy lifestyle choices provides the best chance for success in controlling acne effectively.