Infected Pimple: What It Looks Like, Causes & Treatment

Understanding Infected Pimples
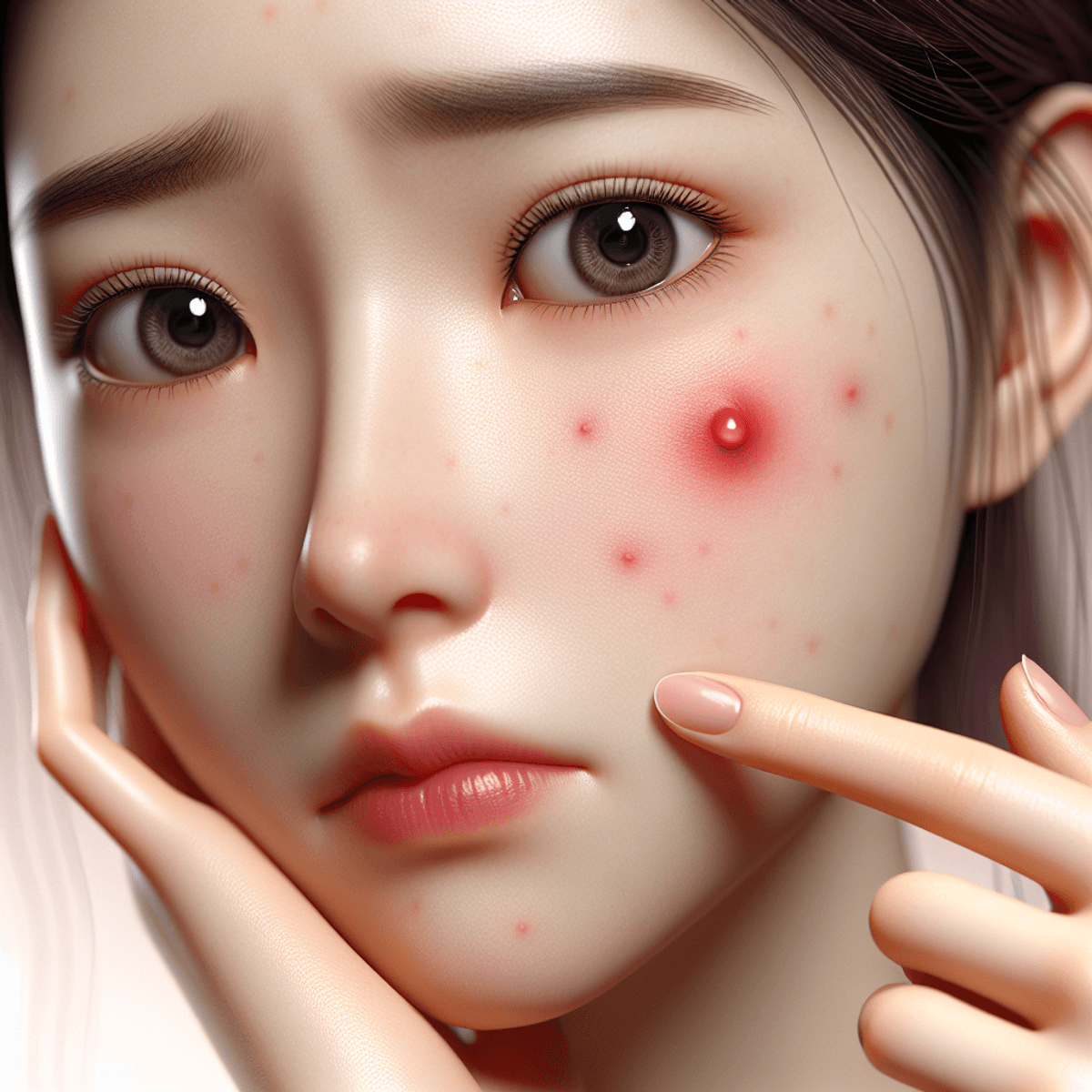
An infected pimple occurs when bacteria infiltrate the skin, typically after popping or squeezing an existing acne lesion. These pimples are often larger, red, swollen, and filled with pus. Recognizing them is crucial for effective treatment and to prevent further complications.
Importance of Prompt Recognition and Treatment
- Prevent complications: Infected pimples can lead to more severe skin issues if left untreated.
- Reduce pain and inflammation: Early intervention can alleviate discomfort.
- Promote faster healing: Addressing infections promptly aids in quicker recovery.
What You’ll Learn from This Article
This article will provide insights into:
- Identifying the key characteristics of infected pimples
- Understanding their causes
- Exploring treatment options
- Discovering long-term strategies for clear skin
By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to get rid of pimples, effectively manage breakouts, and adopt practices for maintaining healthy skin.
Identifying Infected Pimples
Recognizing the symptoms of an infected pimple is essential for effective treatment. The appearance of an infected pimple differs significantly from that of a regular one. Here are the key characteristics to look out for:
- Redness: Infected pimples typically exhibit pronounced redness surrounding the lesion. This intense coloration indicates inflammation and irritation caused by bacteria.
- Swelling: Increased swelling accompanies the redness. The affected area may feel raised and tender to touch, signaling a more serious issue than standard acne.
- Pus-filled heads: Many infected pimples develop a visible pus-filled head. This accumulation of pus results from the body’s immune response to infection, indicating that bacteria have invaded the site.
Differentiating Between Infected and Regular Pimples
Understanding how to differentiate between an infected pimple and a regular one can prevent complications. Here are some distinctive features:
- Size: Infected pimples tend to be larger than typical acne lesions. Their increased size often correlates with the severity of inflammation and infection.
- Pain Level: While both types can cause discomfort, infected pimples usually result in heightened pain or sensitivity. You may notice that even light pressure causes considerable discomfort.
- Duration: Regular pimples often resolve within a few days to a week. In contrast, infected pimples may take longer to heal due to ongoing inflammation and bacterial activity.
- Systemic Symptoms: Severe cases of infected pimples might present additional symptoms like fever or fatigue, which are rarely associated with non-infected acne.
- Color Variation: While normal pimples may show some redness, an infected pimple often has a deeper red hue surrounding it, indicating increased blood flow as part of the immune response.
Recognizing these symptoms of an infected pimple allows for timely intervention, preventing further complications such as scarring or systemic infections. If you observe these signs, consider implementing appropriate treatments or seeking medical advice when necessary.
Being informed about how an infected pimple looks helps you manage your skin health effectively. By paying attention to the appearance and characteristics of your breakouts, you can make better decisions about care and treatment options moving forward.
Cystic Acne – A Severe Form of Infected Pimples
It’s important to note that some infected pimples can evolve into more severe forms such as cystic acne. This condition is characterized by large, painful lumps beneath the skin’s surface and often requires professional medical treatment.
Additional Considerations
In some cases, external factors such as insect bites can also lead to skin infections resembling those of an infected pimple. For instance, a fire ant sting can cause similar symptoms including redness, swelling, and pus-filled blisters. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider all possible causes when diagnosing skin issues.
Causes Behind Infected Pimples
Infected pimples arise primarily due to the introduction of bacteria into the skin. This often occurs when there is a disruption in the skin’s surface, commonly from actions like popping or squeezing existing pimples. Understanding these causes is essential for preventing and managing infected acne effectively.
Primary Cause: Introduction of Bacteria
When a pimple forms, it is essentially an inflamed hair follicle filled with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. The presence of these bacteria is normal; however, an infection occurs when the bacteria penetrate deeper into the skin through breaks in the surface. Once bacteria enter this open wound, they multiply rapidly, leading to inflammation and pus formation.
Role of Popping or Squeezing Pimples
Popping or squeezing pimples significantly increases the risk of developing an infection. When you apply pressure to a pimple, you can inadvertently push bacteria deeper into the skin layers, creating an environment ripe for infection. Additionally, this action disrupts the healing process and may cause further inflammation.
Some key points regarding this behavior include:
- Increased Risk: Squeezing releases bacteria from inside the pimple into surrounding areas.
- Trauma to Skin: Physical manipulation causes micro-tears that allow bacteria easier access.
- Prolonged Healing: An infected pimple takes longer to heal compared to one left untouched.
Other Contributing Factors
In addition to bacterial introduction and physical manipulation, various factors can contribute to acne flare-ups and increase susceptibility to infected pimples:
- Hormones: Fluctuations in hormonal levels, particularly during puberty or menstrual cycles, can lead to increased oil production in skin glands. This excess oil can clog pores and create an environment conducive for bacteria growth.
- Stress: Elevated stress levels can affect hormone regulation and trigger acne outbreaks. Stress-induced hormonal changes may also lead to inflammation in existing pimples.
- Dietary Influences: Certain foods may exacerbate acne conditions in some individuals. High-glycemic index foods and dairy products have been linked with increased acne severity.
Understanding these causes empowers you to take proactive steps in your skincare routine. Awareness of how behaviors like popping pimples contribute to infections allows for better management of acne overall. By keeping your hands away from your face and being mindful of hormonal changes or dietary choices, you can reduce your chances of developing infected pimples significantly.
Risk Factors for Developing Infected Pimples
Certain skin conditions can increase the risk of developing infected pimples. Understanding these factors helps in taking preventive measures. Key conditions include:
1. Cystic Acne
This severe form of acne results in large, painful lumps beneath the skin’s surface. The inflammation associated with cystic acne increases susceptibility to bacterial infections, particularly if the cysts are manipulated or popped.
2. Rosacea
Individuals with rosacea often experience redness, sensitivity, and visible blood vessels. The compromised skin barrier may lead to increased irritation and infections when acne lesions develop.
Other risk factors that contribute to infection development include:
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, especially during puberty or menstrual cycles, can trigger acne breakouts and increase vulnerability to infections.
- Stress: Stress can worsen existing skin conditions, leading to more frequent breakouts and greater chances of infection.
Recognizing these risk factors is crucial for managing your skin health effectively. With this understanding, you can adopt targeted strategies to minimize the likelihood of developing infected pimples.
Healing Process: What to Expect with Infected Pimples
Infected pimples present specific symptoms that differentiate them from regular acne. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for effective treatment and management.
Common Symptoms of Infected Pimples
- Pain: One of the most pronounced symptoms is tenderness or pain in the affected area. This discomfort can range from mild to severe, often worsening with touch.
- Inflammation: The skin around the infected pimple typically appears swollen, contributing to a raised appearance. This is a result of the body’s immune response to the bacterial infection.
- Redness: The area surrounding the pimple may exhibit significant redness, indicating irritation and inflammation.
- Pus Formation: Infected pimples often develop a pus-filled head, which may vary in size. The presence of pus signals an accumulation of white blood cells fighting off the infection.
- Warmth: The affected skin can feel warm to the touch due to increased blood flow as part of the inflammatory response.
Duration of Healing Process
The healing time for infected pimples depends on several factors, including the severity of the infection and individual skin type.
Mild Cases
Healing typically occurs within 5 to 10 days when proper at-home care is implemented. Keeping the area clean and applying warm compresses can facilitate drainage and speed up recovery.
Severe Cases
For more serious infections, healing may take two weeks or longer. Severe cases often require additional medical treatments, such as topical or oral antibiotics, which can extend recovery time.
Understanding these symptoms and their healing timelines allows you to monitor your condition effectively. Early recognition can lead to prompt treatment, potentially reducing the risk of complications such as scarring or further infections. Adopting a proactive approach in caring for your skin will contribute significantly to managing infected pimples efficiently.
Treatment Options for Infected Pimples
1. At-home Treatments
When dealing with infected pimples, prompt and effective treatment is essential. At-home treatments can help manage the symptoms and promote healing, particularly in mild cases. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Maintain Cleanliness
- Keeping the infected area clean is crucial. Use a gentle cleanser that does not irritate your skin. This helps remove any dirt or bacteria that could worsen the infection. Avoid harsh scrubs or exfoliants, as they can exacerbate inflammation and delay healing.
- Warm Compresses
- Warm compresses are beneficial for facilitating drainage of pus without the need to pop the pimple. Soak a clean cloth in warm water and apply it to the affected area for about 10-15 minutes. The warmth helps soften the skin and encourages natural drainage, which can alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling.
- Topical Treatments
- Over-the-counter topical treatments containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can be effective in reducing bacteria and promoting healing. Apply these products only to the infected area, following the instructions on the label.
- Avoid Popping
- Resisting the urge to pop or squeeze pimples is vital in preventing further infection. Popping a pimple introduces more bacteria into the skin, leading to increased redness, swelling, and pain.
Medical Treatments
In cases where at-home remedies do not yield improvement or if symptoms worsen, seeking medical advice may be necessary.
- Prescription Antibiotics
- A healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotics if there is significant infection present. Oral antibiotics can help combat bacteria internally, while topical antibiotics may also be applied directly to inflamed areas.
- Corticosteroid Injections
- For severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections can reduce swelling and pain rapidly. This option is usually employed when other treatments are ineffective.
- Drainage Procedures
- In certain cases, especially where a large amount of pus has accumulated, a doctor may recommend drainage procedures. This involves making a small incision to allow pus to escape safely without further damaging surrounding tissue.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing when you need professional help is critical in managing infected pimples effectively:
- Severe pain that does not improve with at-home treatment.
- Increased redness and swelling spreading beyond the original site.
- Symptoms such as fever or fatigue suggesting systemic infection.
- Infection located near sensitive areas like eyes or mouth.
Prompt attention from a healthcare provider can prevent complications from severe infections.
By understanding these treatment options—both at home and through medical intervention—you empower yourself to manage infected pimples effectively. Proper hygiene practices lay the foundation for successful treatment while minimizing future occurrences of infections associated with acne.
2. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments play a significant role in addressing infected pimples, particularly when combined with at-home treatments. These approaches can vary in effectiveness based on the severity of the infection.
1. Mild Infections
At-home treatments are often sufficient for mild infections. Regular use of a gentle cleanser and warm compresses can facilitate healing while topical antiseptics and benzoyl peroxide reduce bacterial presence.
2. Severe Cases
If symptoms worsen or fail to improve, medical treatments may be necessary. A healthcare provider might recommend stronger topical antibiotics or oral medications depending on the infection’s severity.
Incorporating these topical treatments into your skincare routine will enhance your ability to manage infected pimples. Remember to monitor your skin’s response and adjust treatments as needed to achieve optimal results.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing when an infected pimple requires professional care is crucial. While many mild infections can be managed with at-home treatments, certain signs indicate the need for medical intervention.
Key Indicators for Seeking Help:
- Location of the Infection: If the infected pimple is near the eyes, immediate medical attention is necessary. The delicate nature of this area makes it susceptible to complications.
- Severe Pain: Intense discomfort that persists despite home treatment should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider. Pain levels can be a strong indicator of infection severity.
- Systemic Symptoms: Symptoms like fever, chills, or fatigue accompanying an infected pimple signal a more serious issue that requires medical evaluation.
- Prolonged Healing Time: If an infected pimple does not show signs of improvement within a few days of applying warm compresses and using a gentle cleanser, it’s time to consult a physician.
Medical treatments may include prescribed antibiotics or stronger topical medications tailored to combat the infection effectively. These approaches differ from at-home treatments like gentle cleansers and warm compresses, which are suitable for mild infections.
Understanding these signs helps you navigate when to escalate your treatment strategy. Prioritizing timely medical care can prevent complications and ensure effective healing.
Long-term Strategies for Clear Skin: Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining clear skin involves a multi-faceted approach that goes beyond treating individual pimples. Implementing long-term strategies can significantly reduce the risk of developing infected pimples and enhance your skin’s overall health.
Balanced Diet and Hydration
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in skin health. Consider focusing on:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Foods like berries, spinach, and carrots can help combat inflammation.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil to nourish your skin from within.
- Hydration: Drinking adequate water daily helps maintain moisture levels in the skin. Aim for at least 8 glasses a day to support optimal skin function.
The connection between diet and acne is significant. High glycemic index foods, such as white bread and sugary snacks, may worsen acne conditions. Opt for whole grains, legumes, and lean proteins to stabilize blood sugar levels.
Popular Natural Remedies
In addition to a balanced diet, several natural remedies have gained popularity for their effectiveness in promoting clear skin:
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antibacterial properties, tea tree oil can be applied topically to help reduce inflammation and kill acne-causing bacteria. Dilute with a carrier oil before application to prevent irritation.
- Aloe Vera: Widely recognized for its soothing properties, aloe vera gel can hydrate the skin while also providing anti-inflammatory benefits. Apply directly to the affected areas for relief from irritation.
- Honey: A natural antibacterial agent, honey can be used as a mask or spot treatment. Its moisturizing properties also aid in keeping the skin hydrated.
Implementing these natural remedies into your skincare routine may yield positive results over time.
Consistency in Skincare Routine
Developing a consistent skincare routine is essential for long-term success. Key components of an effective routine include:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild cleanser twice daily to remove dirt without stripping the skin of its natural oils.
- Moisturizing: Even if you have oily skin, maintaining moisture is vital. Choose non-comedogenic moisturizers suited to your skin type.
- Sun Protection: Daily use of sunscreen protects against UV damage that can exacerbate acne issues.
Staying committed to these practices fosters an environment conducive to healthy skin while minimizing the occurrence of infected pimples.
Preventing Future Infections: Hygiene Practices and Skincare Products
Maintaining proper hygiene practices and selecting suitable skincare products are vital steps in preventing future infections, including infected pimples. Avoiding certain habits and adopting a consistent cleansing routine can significantly reduce the risk of acne flare-ups and subsequent bacterial infections.
Essential Practices to Avoid Future Infections
- Avoid Popping Pimples: Refraining from popping or squeezing existing pimples is crucial. This action introduces bacteria into the skin, leading to infections. Instead, focus on allowing blemishes to heal naturally.
- Clean Hands: Always wash your hands before touching your face. Clean hands prevent the transfer of bacteria and dirt to your skin, reducing the risk of infection.
- Use Clean Towels: Ensure that any towel you use to dry your face is clean. Dirty towels can harbor bacteria, increasing the likelihood of infection.
- Change Pillowcases Regularly: Pillowcases collect oils, skin cells, and bacteria over time. Change them weekly to minimize exposure to these irritants while you sleep.
Choosing Non-Irritating Skincare Products
Selecting gentle, non-comedogenic products is essential for maintaining healthy skin. Look for labels that indicate:
- Non-Comedogenic: These products are formulated not to clog pores, which helps prevent acne formation.
- Fragrance-Free: Fragrance can irritate sensitive skin and contribute to breakouts. Opt for fragrance-free options whenever possible.
- Alcohol-Free: Alcohol-based products can strip natural oils from the skin, leading to dryness and irritation. Choose alcohol-free cleansers and toners.
Daily Skincare Routine Tips
Establishing a consistent daily skincare routine plays a significant role in minimizing acne occurrences. Follow these recommended steps:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild cleanser twice daily (morning and night) to remove dirt and excess oil. Avoid harsh scrubs that could irritate the skin.
- Exfoliation: Exfoliate once or twice a week with a gentle exfoliant containing alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs). This helps remove dead skin cells without causing irritation. Be cautious not to over-exfoliate as it can lead to increased sensitivity.
- Moisturization: Even if you have oily skin, using a lightweight moisturizer is vital for maintaining hydration. Look for oil-free formulas that won’t clog pores.
- Sun Protection: Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days. Sun protection helps prevent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from previous acne marks.
- Spot Treatments: If breakouts occur, apply targeted treatments containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid directly onto blemishes. Use these sparingly and follow product instructions carefully.
- Nighttime Routine: Incorporate retinoids or retinol into your nighttime skincare routine gradually if your skin tolerates it well. These ingredients help promote cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.
Following these practices and routines not only enhances your overall skin health but also contributes significantly to preventing future infections related to acne. Regular adherence will create a healthier environment for your skin, minimizing the risk of developing infected pimples in the future.
By understanding how hygiene practices intertwine with effective skincare products, you empower yourself with knowledge that leads to clearer skin over time.
Conclusion
Maintaining proper skincare habits is essential for preventing infected pimples and promoting overall skin health. Consider the following practices:
- Avoid Popping Pimples: This simple action can significantly reduce your risk of introducing bacteria into the skin.
- Cleanse Regularly: Use a gentle cleanser to keep your skin free from dirt and excess oil.
- Moisturize Daily: A good moisturizer helps maintain skin hydration and barrier function.
- Choose Non-Irritating Products: Opt for skincare products that are labeled as non-comedogenic to avoid clogging pores.
Incorporating these habits into your daily routine not only supports clear skin but also enhances your confidence. By being mindful of how you care for your skin, you can minimize the occurrence of infections and ensure a healthier complexion moving forward. These proactive measures empower you to take control of your skincare journey.